[May'24 - Jun'24]
Semantic Image Segmentation using Deep Learning and U-Net Architecture
In this project, I have built a U-Net, a specialized Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) designed for precise, pixel-level image segmentation. The objective is to predict a label for every single pixel in an image, specifically using data from a self-driving car dataset.
What is Semantic Image Segmentation?
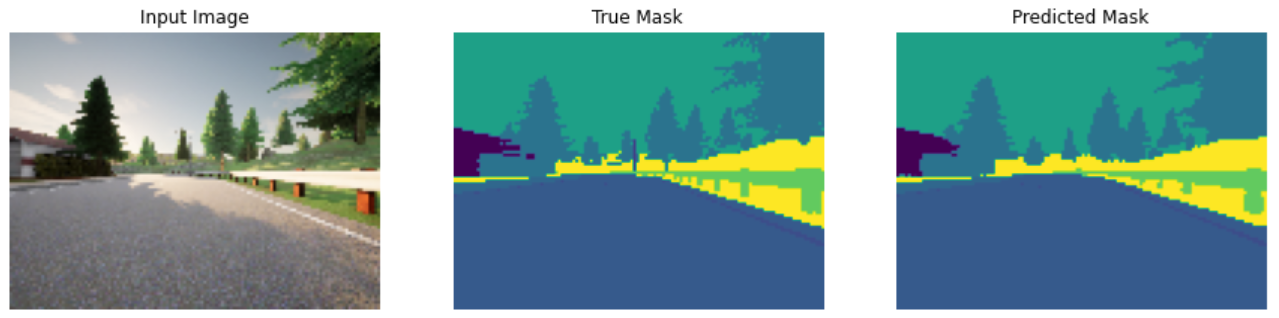
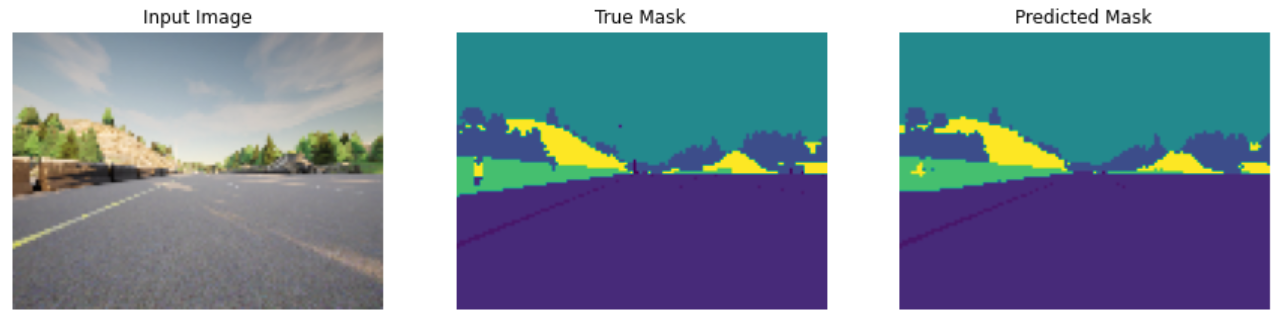
Semantic image segmentation is a form of image classification that, unlike object detection which uses bounding boxes, labels each pixel in the image with a corresponding class. This method provides a much finer and accurate understanding of the image by creating a precise mask for each object. For instance, in our dataset, the "Car" class is marked with a dark blue mask, and the "Person" class is marked with a red mask.
This level of detail is crucial for self-driving cars, which need to interpret their surroundings with pixel-perfect accuracy to navigate safely. They must recognize and differentiate between various objects such as other cars, pedestrians, and obstacles to make informed decisions like changing lanes or avoiding hazards.
The U-Net Architecture
The U-Net architecture, first proposed in 2015 for biomedical image segmentation, has proven highly effective for semantic segmentation tasks. Its architecture consists of three main parts:
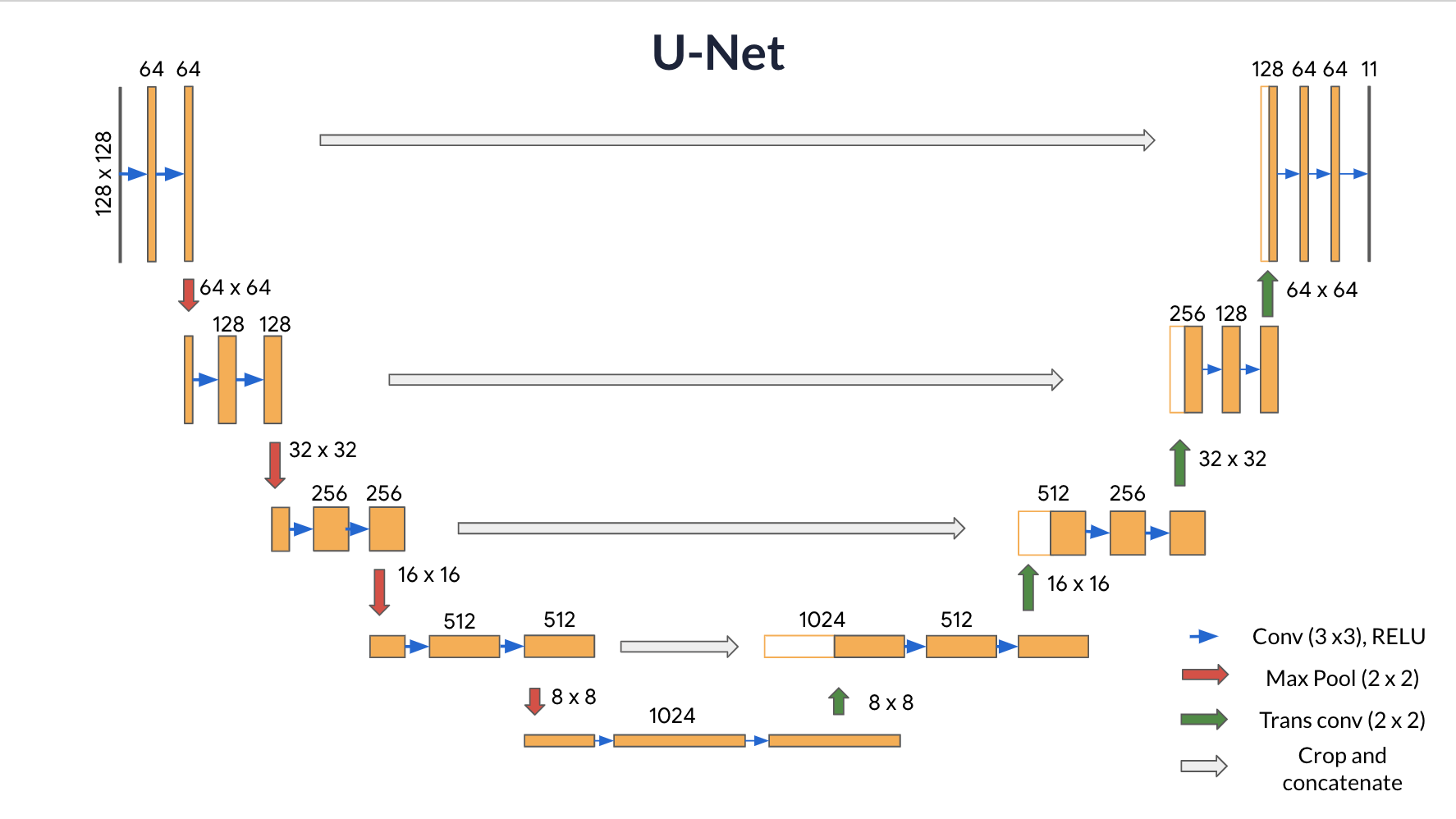
Contracting Path (Encoder containing downsampling steps):
Expansive Path (Decoder containing upsampling steps):
Final Feature Mapping Block:
In the final layer, a 1x1 convolution is used to map each 64-component feature vector to the desired number of classes. The channel dimensions from the previous layer correspond to the number of filters used, so when you use 1x1 convolutions, you can transform that dimension by choosing an appropriate number of 1x1 filters. When this idea is applied to the last layer, you can reduce the channel dimensions to have one layer per class.
The U-Net network has 23 convolutional layers and 8,640,471 (trainable) parameters. The model can be used for various applications, such as autonomous driving, medical imaging, and satellite image analysis.
Implementation Details
For this project, I implemented semantic image segmentation on the CARLA self-driving car dataset. The dataset consists of images captured from a simulated urban driving environment, providing a diverse and challenging set of scenarios for training the model.
Steps Involved in the Project:
-
Data Preparation:
- Preprocessing the CARLA dataset to create training and validation sets.
- To make the input uniform, convert any input image to shape (96, 128).
-
Building the U-Net Model:
- Implementing the U-Net architecture from scratch using tensorflow a deep learning framework.
- Configuring the model with "SparseCategoricalCrossentropy" loss function and "adam" optimization techniques to handle multi-class segmentation.
-
Training the Model:
- Training the model on the prepared dataset.
- Monitoring training with "accuracy" metric to ensure the model learns to segment correctly.
- The model is trained for 30 epochs with a batch size of 32.
-
Evaluation and Results:
- Testing the model on unseen data to evaluate its performance.
- Visualizing the results by comparing the predicted masks with the true masks to assess the accuracy and quality of the segmentation.