Guide: Srikrishna S
[May'23 - July'23]
Find detailed project report here.
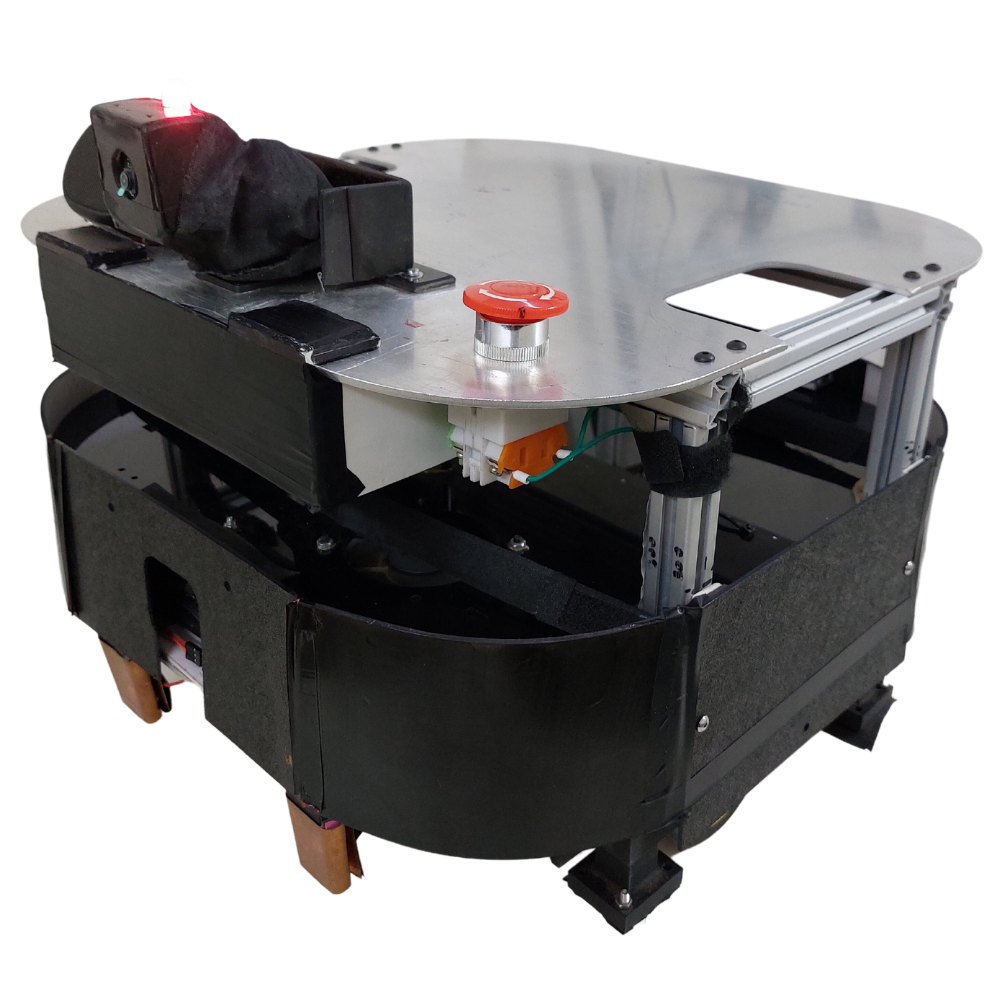
The "Development of TeleOperation and TeleObservance Robot" project marks a remarkable journey into the realm of robotics and autonomous systems. Our team at SeiAnmai Tech. collaborated to create an innovative mobile platform capable of autonomous navigation and seamless teleoperation, tailored to address the growing demands of various real-world applications.
Guided by our vision for a versatile robotic system, we set out to design a robot that could operate efficiently without human intervention, while also incorporating features that enable intuitive remote control and observation. The foundation of our robot was built upon the powerful Robot Operating System (ROS2) Humble, providing a robust framework for the integration of diverse functionalities.
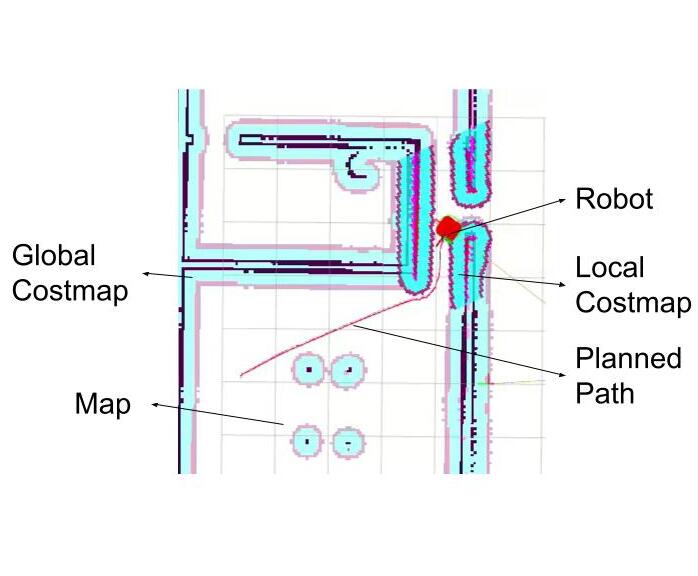
Navigating through dynamic and static obstacles with confidence, the robot demonstrated its autonomy through Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) techniques. The integration of micro-ROS with Raspberry Pi Pico was implemented using a Docker container in C language which allowed for seamless communication between the high-level ROS2 environment and the low-level hardware, enhancing the robot's adaptability and responsiveness.
Autonomous docking, driven by Aruco marker detection, showcased the robot's intelligence as it effortlessly navigated and docked with precision. This cutting-edge application exemplified the potential of robotics in practical scenarios.
Throughout the development process, meticulous calibration of motors and fine-tuning of PID control algorithms laid the foundation for the robot's stable and accurate movements. Extensive testing and debugging ensured the system's robustness, making it adaptable to diverse environments and scenarios.
The complete setup was implemented using the Robot Operating System (ROS2 Humble) framework. The primary rationale behind this choice was the ability to reuse code, achieve modularity, and enable seamless communication among different modules.